Impact of Computational Parameter on Aerodynamics Forces on the Sedan Car Model
Keywords:
Aerodynamics, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Drag coefficient, Lift coefficientAbstract
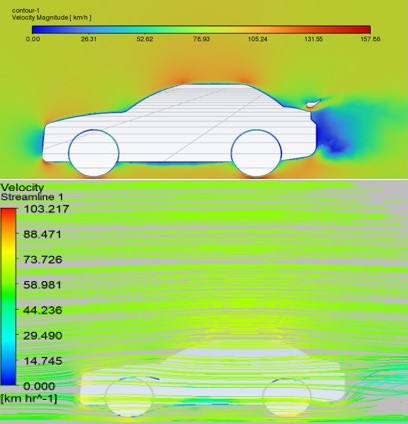
A spoiler is an aerodynamic component designed to reduce drag in automobiles. The main purpose of a rear car spoiler is to enhance the vehicle's grip on the road by reducing aerodynamic drag and increasing stability. Positioned at the rear, it creates a high-pressure zone to counteract the low pressure on the trunk, thereby improving stability. This study aims to investigate the effects of rear spoilers on aerodynamic drag and stability, considering the Malaysian National Speed Limit. Both the sedan vehicle model and the rear spoiler models were created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, SolidWorks and the data was analyzed using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software to calculate drag and lift forces at speeds of 60 km/h, 90 km/h, and 110 km/h. Certain limits were provided by the design's intricacy. Together with the sedan car, the simulations featured two different rear spoiler designs: the rear wing and the ducktail spoiler. The rear wing significantly increased drag and downforce, but the ducktail spoiler only slightly increased both, according to the results. Rear spoilers also boost downforce. In addition, cars that moved more slowly than those that moved quicker showed more drag. In conclusion, spoilers only help at very high speeds; at lower speeds, they create drag. Spoilers are useful under the Malaysian National Speed restriction, especially on motorways with a 110 km/h speed restriction. The results indicated that a sedan car without a spoiler had a drag coefficient, Cd of 0.5 and lift coefficient, Cl of -1.5. In contrast, a sedan car with a spoiler had a Cd of 0.2 and Cl of -0.2.