Numerical Study of Flow and Heat Transfer on Plate-Fin Heat Exchanger in a High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor
Keywords:
plate heat exchanger, heat transfer, CFD, k-epsilon, plain, staggeredAbstract
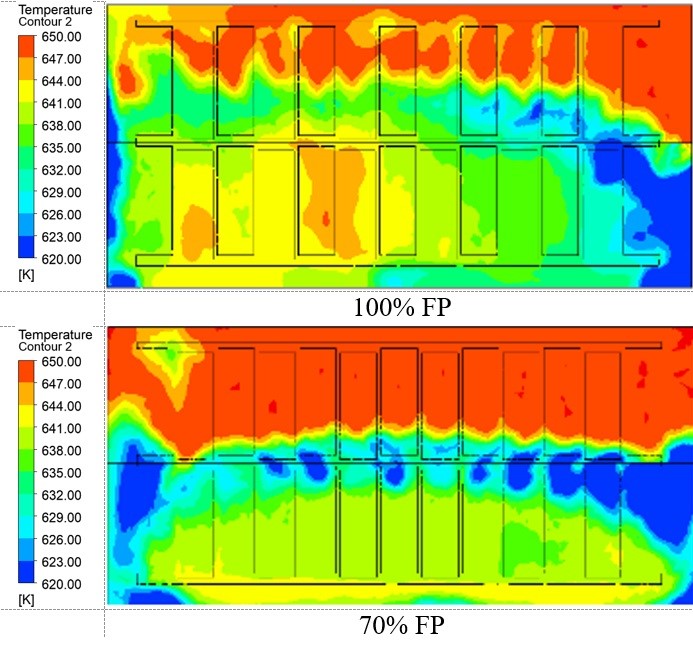
Plate heat exchangers, known for their high efficiency and low mass, are a type of compact heat exchanger widely used in aerospace, automotive, and power machinery applications. The objective of this study is to model both plain and staggered fin configurations and to analyze the flow characteristics and heat transfer within a plate-fin heat exchanger. The analysis focuses on examining fluid dynamics and evaluating heat transfer efficiency, contributing to the optimization of plate-fin heat exchanger designs for various industrial applications. The analyses utilize Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) approaches to evaluate heat transfer of the heat exchanger. The simulation uses models including the energy equation and the k-epsilon viscous model. The SIMPLE method is used for solving equations to ensure accurate pressure calculations. At various power levels, Model 2 consistently shows better temperature distribution in terms of uniformity and clearer separation between hot and cold zones compared to Model 1, demonstrating superior heat exchanger performance due to its staggered fin design. Moreover, both models have high upper section velocities promoting efficient heat transfer, with Model 1's lower section showing slower velocities and higher thermal exchange, while Model 2's staggered fins enhance overall heat exchange and turbulence. Therefore, the study concludes that staggered fins (Model 2) are more effective for applications that require high heat transfer efficiency compared to plain fins (Model 1) in HGTR.