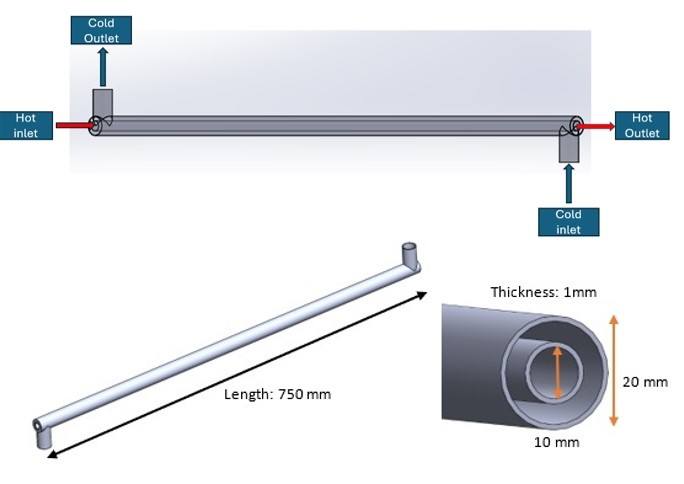
Double Straight Tube Counter-Flow Heat Exchanger for Optimum Heat Transfer by Numerical Simulation
Keywords:
CFD Simulation, double straight tube counter-flow, heat exchanger, k-ω turbulenceAbstract
The study provides a complete computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis of a twin straight tube counter-flow heat exchanger. The study sought to evaluate the temperature, velocity, and pressure distributions within the heat exchanger under various input circumstances for hot and cold fluids. The key goals were to predict heat transfer and flow behavior with advanced CFD techniques such defined boundary conditions, geometric modelling, and producing a computational grid. The study technique used CAD software to build the heat exchanger shape and implemented the k-ω turbulence model in CFD simulations. The simulation results were thoroughly tested against experimental data to demonstrate the CFD model's reliability and accuracy. The average errors were 0.52% for the hot fluid outlet temperature, 8.15% for the cold fluid outlet temperature, and 9.73% for the overall heat transfer rate, with the hot fluid outlet temperature being notably well-matched. The maximum and minimum heat transfer rate obtained from the simulation is 1521.80 W and 1390.88 W respectively. The maximum hot and cold fluid temperature are 62.17°C and 18.79°C respectively. This extensive CFD analysis of the twin straight tube counter-flow heat exchanger gives vital insights into its performance and thermal properties, helping to optimize and enhance this critical industrial equipment. The successful validation of numerical predictions versus actual data emphasizes the need of combining computational and experimental approaches for designing and analyzing heat exchangers. The combination of these techniques can lead to a better understanding of the complicated fluid flow and heat transfer processes within the heat exchanger, allowing for more efficient and dependable designs to be built